June marks National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month, a time dedicated to shedding light on the often misunderstood conditions of migraines and headaches.
In this blog, we'll explore the complexities of these conditions, including their various causes and types. Here's what you need to know about migraines and headaches — and when to seek professional medical help.
What are Migraines?
Migraines are a type of headache disorder characterized by intense, throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head. Unlike typical headaches, migraines are often accompanied by a range of debilitating symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Common symptoms include:
- Throbbing or pulsating pain: Often localized to one side of the head but can occur on both sides.
- Nausea and vomiting: Many migraine sufferers experience gastrointestinal distress.
- Sensitivity to light and sound: Bright lights and loud noises may exacerbate the pain.
- Aura: Some patients experience visual disturbances (such as flashing lights or blind spots) before the onset of a migraine.
Migraines can last anywhere from a few hours to several days. Note that their frequency and severity vary widely, with different people experiencing different symptoms.
What are Headaches?
Headaches, in general, are defined as pain and discomfort in the head or face area. They are one of the most common medical problems and can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, dehydration, or underlying medical conditions.
Understanding the different types of headaches is essential for effective management and treatment of the condition. If you suffer from headaches, you could be experiencing one of the following:
- Tension-Type Headaches: These are the most common type of headache, often described as a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head.
- Cluster Headaches: These are less common but extremely severe headaches that occur in cyclical patterns or clusters.
Types of Headaches and Their Causes
While these conditions can be incredibly disruptive, knowing what triggers them will empower you to take control of your health this National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month. In most patients, the root cause lies in genetic, environmental, or physiological issues.
Causes of Migraines
Migraines are complex and multifaceted, with a variety of factors contributing to their onset. Understanding these causes can help in managing and potentially reducing the frequency of migraine attacks. Research indicates that migraines often run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. If one or both of your parents suffer from migraines, you are more likely to experience them, as well.
Several external factors can also trigger migraines. Common triggers include emotional stress and certain foods or drinks (i.e. alcohol and caffeine). Sensory stimuli like bright lights, loud noises, and strong smells may trigger migraines in certain individuals. Additionally, hormonal changes (particularly in women) might lead to migraines, often correlating with menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
Causes of Tension-Type Headaches
Tension-type headaches are the most common form of headache and are often linked to lifestyle factors or physical strain. The primary cause of tension-type headaches is muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, and scalp.
This tension results from emotional stress, leading to muscle tightness and headaches. If you have poor posture or are sitting in one position for extended periods, it can strain your muscles and lead to headaches.
Another contributor is the prolonged use of digital screens without adequate breaks; this, in turn, creates eye strain that transitions to a tension headache.
Causes of Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are less common but extremely painful, and their exact cause is still not fully understood. During National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month, important research is conducted to find a solution to this mystery.
Current data suggests a potential link to the hypothalamus, a small region at the base of the brain. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating many bodily functions, including the sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm). Abnormalities or disruptions in this area may trigger the cyclical nature of cluster headaches. Moreover, cluster headaches often occur at the same time each day, suggesting a strong link to the body's internal clock.
What Type of Headache Do I Have?
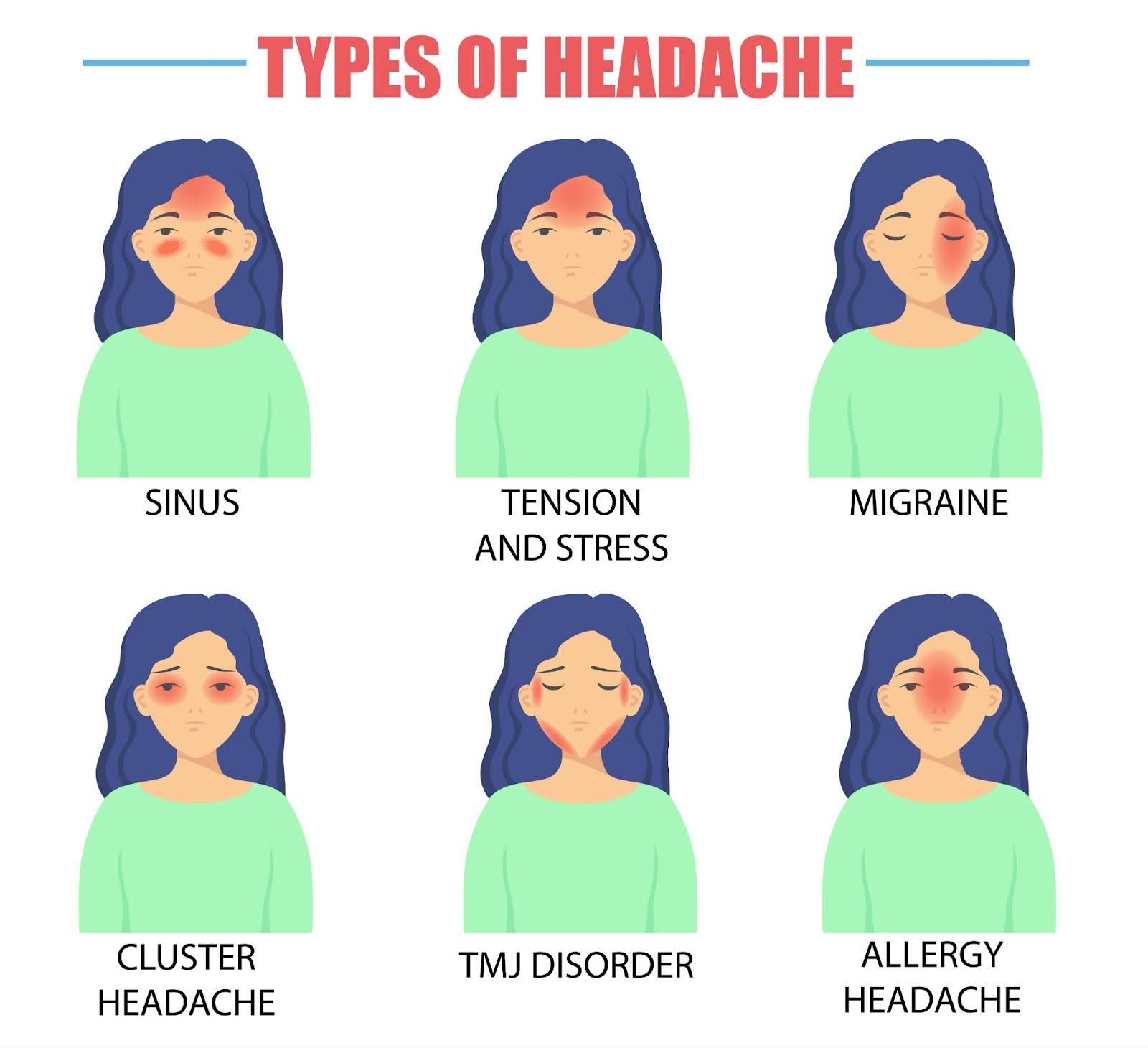
Headaches come in various forms, each with their own set of symptoms. Recognizing the type of headache you are experiencing is crucial for effective treatment. Here are the distinguishing features of tension-type headaches, cluster headaches, and different variants of migraines.
Tension-Type Headaches
Tension-type headaches are among the most commonly experienced by patients, and they are often described as a feeling of bilateral pressure or tightness around the head. This type of headache typically manifests as a constant, dull ache that affects both sides of the head, rather than the pulsating pain associated with migraines.
The discomfort may extend to the neck and shoulders, contributing to an overall sense of stiffness. Unlike migraines, tension-type headaches are not usually accompanied by nausea or sensitivity to external stimuli like light and sound.
Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are less common but are known for their excruciating severity. These headaches are characterized by intense, unilateral pain that is often centered around one eye. The pain can be so severe that it wakes sufferers from sleep, lasting anywhere from 15 minutes to 3 hours at a time.
Cluster headaches occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, with individuals experiencing frequent attacks over weeks or months; these experiences are typically followed by remission periods where the headaches go away. Additional symptoms may include redness and tearing of the eye, nasal congestion, or restlessness.
Migraine Variants
Migraines are a complex type of headache with several variants, the most notable being migraines with aura and migraines without aura.
- Migraines with Aura: This variant is defined by sensory disturbances that precede the headache phase. These disturbances, known as auras, can include visual phenomena such as flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots. Some individuals may also experience tingling sensations, difficulty speaking, or other neurological symptoms. The aura phase typically lasts between 20 minutes to 1 hour, followed by the onset of a migraine headache.
- Migraines without Aura: This is the more common type of migraine, where the headache phase occurs without any preceding sensory disturbances. The pain is usually throbbing and accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines without aura can last from a few hours to several days, greatly impacting daily activities.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a Headache
While occasional headaches can often be managed with over-the-counter medications and lifestyle changes, certain symptoms warrant professional help.
Recognizing Red Flags
Certain headache symptoms should never be ignored, as they may indicate a more serious underlying condition. One such red flag is the sudden onset of a severe headache, often described as a "thunderclap" headache. This type of headache reaches its peak intensity within seconds to minutes; it may be a sign of a serious issue such as a brain hemorrhage or aneurysm. Immediate medical attention is essential in such cases.
Another critical red flag is the presence of accompanying neurological symptoms. These can include confusion, vision loss, difficulty speaking, weakness on one side of the body, or seizures. Such symptoms could indicate a stroke, brain tumor, or other neurological disorders, and require urgent evaluation by a healthcare professional.
When Chronic or Severe Symptoms Persist
If you experience chronic or severe headaches that significantly impact your daily life, it is important to seek medical advice. Headaches that occur frequently, last for extended periods, or are resistant to over-the-counter treatments can be indicative of an underlying condition that needs to be addressed. Persistent headaches will affect your ability to perform everyday activities, making it very important to find an effective treatment plan.
Who to See About Headaches
When seeking help for headaches and migraines, the first step is often to consult your primary care physician. They can perform an initial assessment, rule out any immediate concerns, and provide referrals to specialists if necessary. Primary care physicians are well-equipped to manage common headache types and can offer guidance on lifestyle changes, medications, or other treatments.
For more specialized care, a neurologist is the healthcare professional to see. Neurologists are experts in disorders of the nervous system, including headache disorders. They can provide a more comprehensive evaluation and develop a tailored treatment plan for your specific condition.
Finding Support During National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month

Living with chronic headaches or migraines can be an isolating, exhausting experience. The persistent pain and unpredictability of these conditions often lead to frustration, anxiety, and a sense of helplessness. That's why National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month is so important — to promote the understanding that, above all else, you are not alone in your struggle.
The Emotional Impact
Migraines and headaches can take a significant toll on your mental and emotional well-being. The constant battle with pain may lead to feelings of frustration, as it often disrupts daily activities, work, and social interactions. Recognizing these emotional challenges is the first step towards addressing them and seeking the support you need.
Your Pain is Always Valid
One of the most challenging parts of living with chronic headaches is the misconception that because the pain is invisible, it is somehow imaginary or exaggerated. It's crucial to emphasize that just because others cannot see your pain, it does not make it any less real. Your suffering is legitimate, and you deserve appropriate medical care as with any other health condition.
Open Communication
Discussing your condition openly with healthcare providers ensures that you receive the best possible care and treatment. Be honest about your symptoms, triggers, and the impact on your daily life. This information is key for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
Equally important is building a network of family, friends, or support groups who understand and empathize with your experiences. Sharing your feelings with others who are going through similar challenges can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
Support groups, in particular, offer valuable resources, coping strategies, and a sense of community to support you along your journey.
Find Real Relief with Arnot Health
Remember, you don't have to face this challenge alone. Our team of specialists is dedicated to providing comprehensive care tailored to your needs. Find a provider near you today!

